Outputs: Amps Drawn, Power Used, Power Produced, Efficiency, Heatload, Current
Analytical Work
Theory/governing Equations
|
|
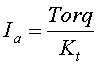
|
Motor constants: –Io = 3A, –R = 0.111W, –Kv = 256 RPM/V |
|
Linking to propeller model
| Converge on RPM using Fixed Point Iteration (FPI) | |
|
|
|
Propeller module in isolation
|
Motor module in isolation
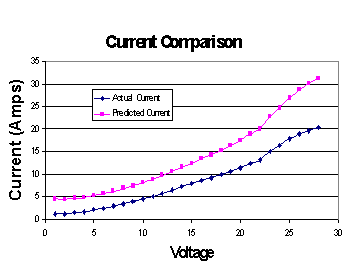
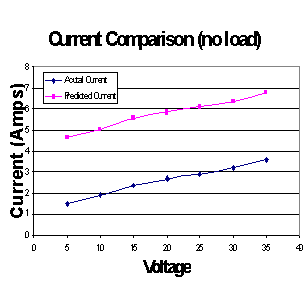
•Torque
calculated based on power used rather than power produced, this
explains the approximate 3A shift between the actual and
predicted
|
•
•
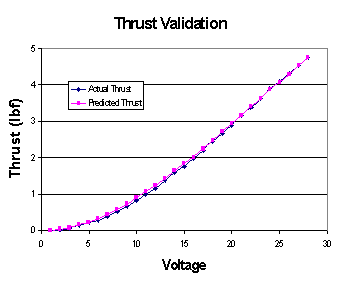
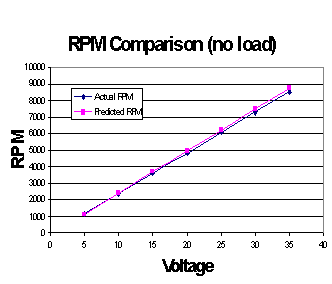
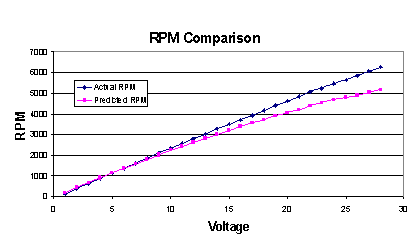
Motor Module Results Comparison
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
Analytical Work
-
Thrust and Power Coefficients - Confirmation of Mathematical Models
-
Experimental Work